Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is quickly becoming commonplace with men over 40, but sometimes the solution to increasing testosterone and improving vitality involves making some simple and effective lifestyle modifications.
Here are five scientifically backed methods for improving testosterone levels in men.
1. Decrease sugar intake.
Research has shown that after meals, testosterone levels decrease. This is perfectly normal. Testosterone fluctuates throughout the day and post-meal decreases are a normal physiological response. Sugar alone has been shown to decrease testosterone levels by approximately 25% one hour after a meal. Since sugar is easily consumed and a component of many processed foods, regular sugar intake depress testosterone levels. Given the inverse relationship of insulin sensitivity and testosterone levels, it is wise to consider eliminating refined sugar from your diet and if you need to sweeten something .
2. Decrease your body fat levels.
Decreasing body fat is an important piece of advice for anyone seeking health improvements. Another great reason: fat tissue converts testosterone into estrogen, something referred to as aromatization. As we age, we tend to increase our body fat levels over time. Having higher levels of estrogens makes it easier for men to add more fat into existing body fat stores, resulting in a vicious cycle. This is one of the main reasons why men may see a decline of testosterone with age since we tend to accumulate body fat stores of time. Decreasing body fat is an effective way to increase testosterone levels in men.
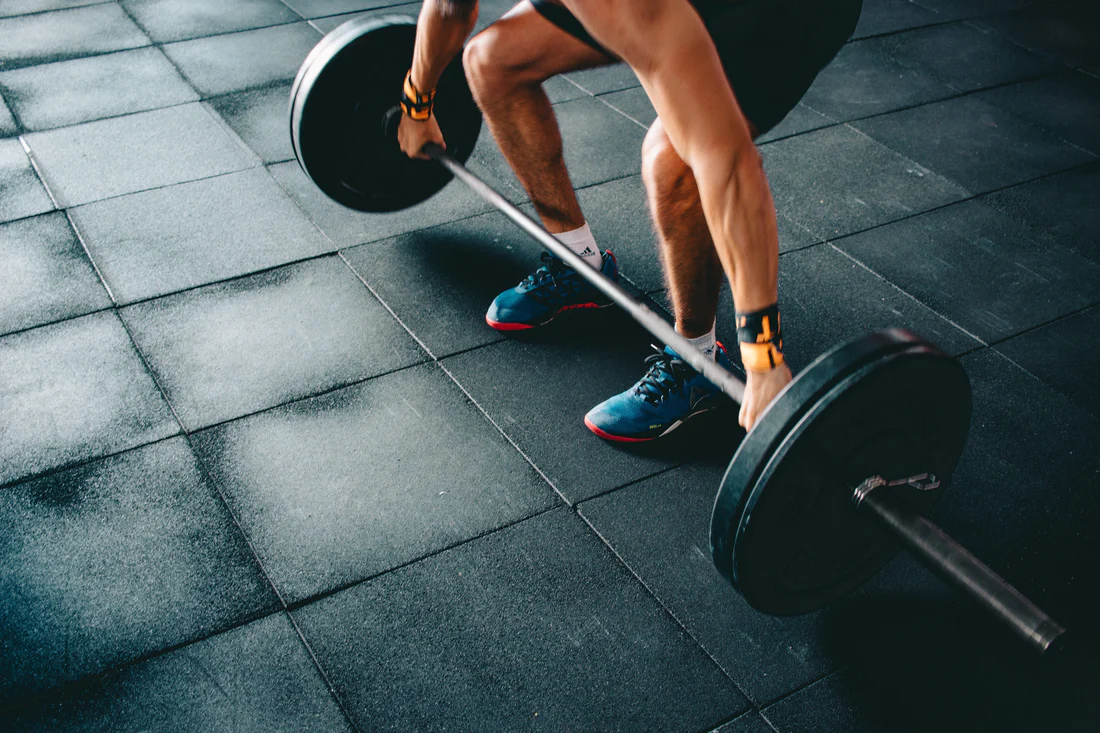
3. Lift heavier weights; take shorter breaks.
Countless studies have demonstrated that bigger lifts lead to bigger acute increases of testosterone post-exercise. This may be because bigger lifts result in greater lactate production which has been directly shown to increase testicular production of testosterone.
If you are not interested in lifting heavy, you can also choose light to moderate weights and work your muscles to fatigue and use shorter rest intervals. This will also help increase testosterone production while simultaneously burning more body fat, thereby providing another avenue for natural testosterone increases.
4. Make sure you are getting enough vitamin D.
In a clinical study looking at men trying to lose weight, participants who were vitamin D deficient showed increased testosterone levels with vitamin D therapy compared to men in the placebo group (not receiving any vitamin D). Though these increases in testosterone were modest, practically speaking, testosterone levels will not improve unless critical aspects of health are addressed. Vitamin D deficiencies can be signs of bigger issues with an individual’s diet or lifestyle, but vitamin D does seem to have a notable relationship with testosterone. If men are not getting enough vitamin D, there can be a direct impact on the production of testosterone.
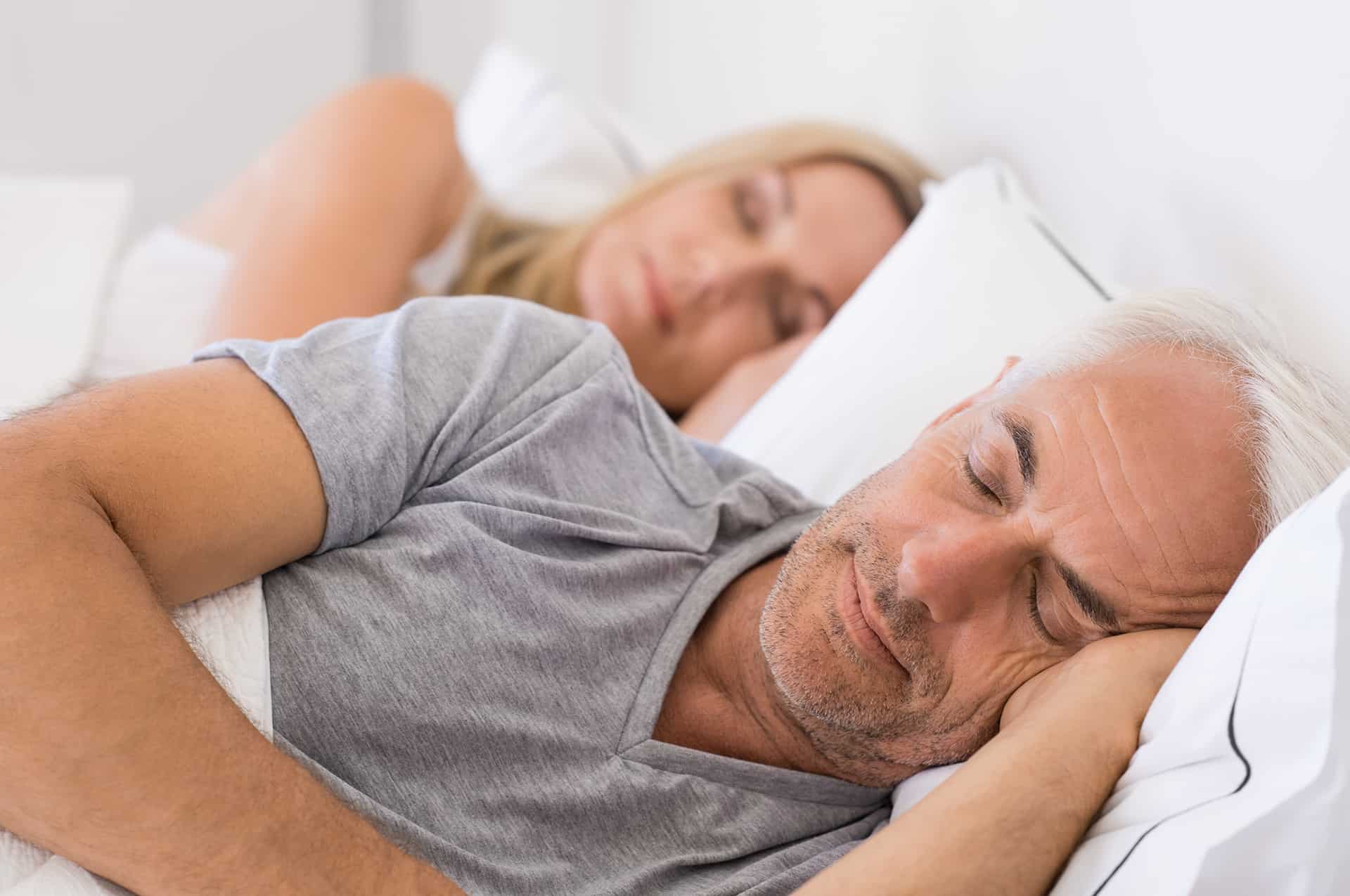
5.Sleep
In older men, morning testosterone levels were linked to sleep; the more they slept, the higher their levels. Duration of sleep was positively associated with total testosterone levels regardless of age, aerobic exercise, and even body fat in adult men ranging from 29-72 years of age. Making sure your body gets the rest it needs by aiming to get a minimum of 8 hours per night can help maximize natural testosterone production.
Your optimum health takeaway
References:
Caronia LM, Dwyer AA, Hayden D, Amati F, Pitteloud N, Hayes FJ. Abrupt decrease in serum testosterone levels after an oral glucose load in men: implications for screening for hypogonadism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2013;78(2):291-6.
Goh VH, Tong TY. Sleep, sex steroid hormones, sexual activities, and aging in Asian men. J Androl. 2010;31(2):131-7.
Lu SS, Lau CP, Tung YF, Huang SW, Chen YH, Shih HC, et al. Lactate and the effects of exercise on testosterone secretion: evidence for the involvement of a cAMP-mediated mechanism. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1997;29(8):1048-54.
Penev PD. Association between sleep and morning testosterone levels in older men. Sleep. 2007;30(4):427-32.
Pilz S, Frisch S, Koertke H, Kuhn J, Dreier J, Obermayer-Pietsch B, et al. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on testosterone levels in men. Horm Metab Res. 2011;43(3):223-5.
Vermeulen A, Goemaere S, Kaufman JM. Testosterone, body composition and aging. J Endocrinol Invest. 1999;22(5 Suppl):110-6.